Interdisciplinary Geography
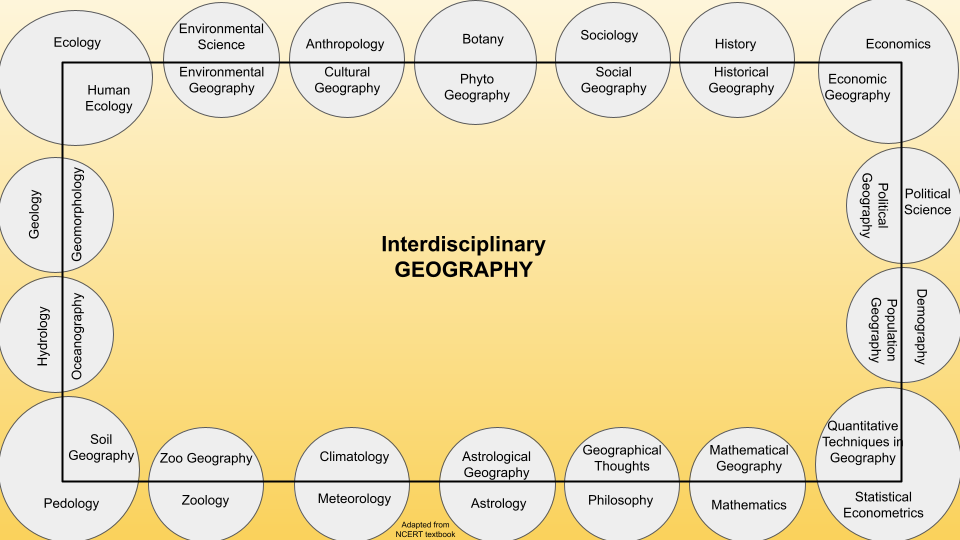 |
Interdisciplinary Nature of GeographyGeography's interdisciplinary nature arises from its comprehensive exploration of the complex interactions between natural and social processes, crucial for understanding the interconnectedness of the world and human-environment relationships. Spatial PerspectiveGeography's focus on space and place encourages the consideration of both physical and human dimensions. This necessitates collaboration between natural and social sciences to comprehensively analyze spatial patterns and relationships. Complex SystemsGeographical phenomena often involve intricate systems that cannot be fully understood by a single discipline. Interdisciplinary approaches help unravel these complexities by integrating insights from multiple fields. Human-Environment InteractionGeography explores how humans interact with their environment, requiring insights from both social and natural sciences to grasp the dynamics of these interactions. Global ChallengesMany global challenges, such as climate change, urbanization, and resource management, require expertise from various disciplines to develop effective solutions. Data AnalysisGeographical research often involves extensive data analysis, which benefits from contributions from disciplines like statistics, remote sensing, and geographic information systems (GIS). Cultural and Behavioral FactorsUnderstanding human behavior, cultural practices, and societal impacts on landscapes involves knowledge from social sciences like anthropology, sociology, and economics. Sustainable DevelopmentGeography plays a crucial role in understanding and promoting sustainable development, which necessitates knowledge from both natural and social sciences. Policy and Decision-MakingGeographic information and analysis are vital for policy formulation and decision-making in various sectors, including urban planning, disaster management, and environmental conservation. Landscape ChangeStudying changes in landscapes requires expertise in both the physical processes driving change and the social factors influencing land use. Regional StudiesGeography often involves studying specific regions, which requires considering diverse factors such as climate, history, culture, economics, and geopolitics. In essence, geography's interdisciplinary nature allows it to address complex real-world issues, bridge gaps between different fields of study, and provide holistic insights into the interactions shaping our planet. |